|
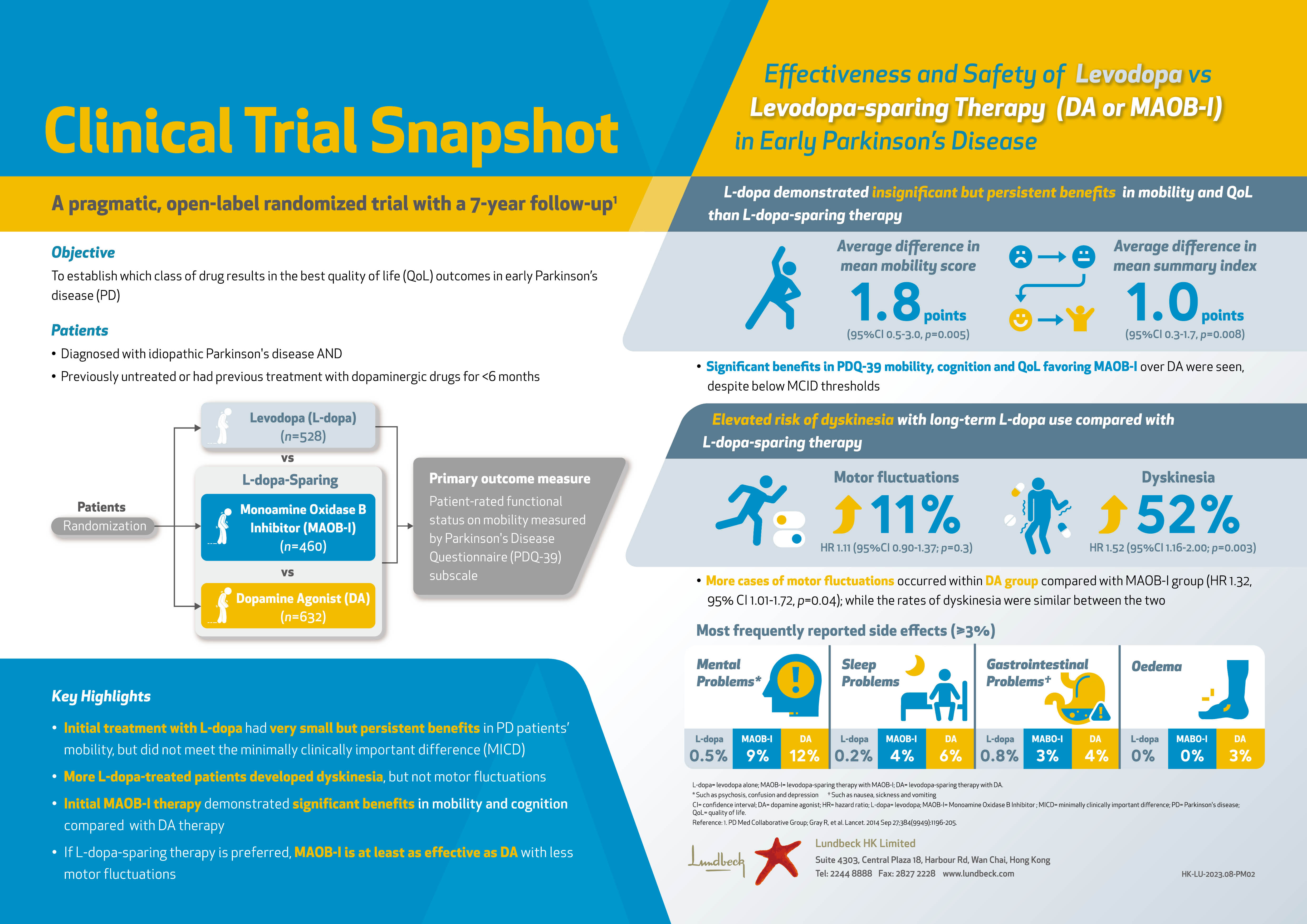
| Adult patients with active ankylosing spondylitis (AS) treated with intravenously (IV) administered an anti-tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) monoclonal antibody, golimumab (GOL), demonstrated improvements in sleep problems, total back pain (TBP) and night back pain (NBP). Results were presented at the 2017 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) / The Association of Rheumatology Professionals (ARP) Annual Meeting held in Atlanta, Georgia. |
 |
| This was a phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial including 208 patients ≥18 years with a diagnosis of definite AS and a Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) score ≥4, TBP on the visual analog scale (VAS) ≥4 and a C-reactive protein (CRP) level of ≥0.3 mg/dL. Patients were randomized at baseline to receive either IV GOL 2 mg/kg (n=105) at week 0, 4 and every 8 weeks or placebo (n=103) at week 0, 4 and 12, with a crossover to GOL at week 16 through week 52. The Medical Outcomes Study-Sleep Scale (MOS-SS, range 0-100) was a generic instrument used to assess six dimensions of sleep including: sleep disturbance, somnolence, sleep adequacy, snoring, awaken short of breath or headache and quantity of sleep during the past 4 weeks. As a result of these six dimensions, a composite Sleep Problems Index (SPI) was generated and it was indicated that an increase in score from baseline represented improvement. TBP and NBP over the past week were assessed using VAS (0-10 cm; 0=no pain, 10=severe pain). Results presented here are from weeks 8 to 28. |
 |
| SPI Mean changes in SPI demonstrated a significantly greater mean improvement in GOL compared to placebo at weeks 8 and 16 (p<0.001), whereas after switching placebo to GOL at week 28, the differences diminished between both groups, GOL and placebo. TBP and NBP Mean improvements from baseline to weeks 8 and 16 in patient’s assessment of TBP (cm) were greater in GOL than placebo (p<0.001), and after placebo switched to GOL, the differences diminished at week 28. Additionally, mean improvements at week 8 and 16 from baseline in patient’s assessment of NBP (cm) were also greater in GOL than placebo (p<0.001), and differences diminished at week 28 after switching placebo to the GOL treatment. |
| Summary of mean changes in SPI, TBP and NBP from baseline |
 |
| *At week 28, placebo has crossed over to GOL. |
| Change in NBP was associated with change in SPI at weeks 8, 16 and 28 with a p-value of 0.002, 0.001 and 0.031, respectively. In the general linear model, most of the association between change in TBP and change in SPI was explained by the association between change in NBP and change in SPI. |
 |
| In this multicenter, randomized trial, administering IV GOL 2 mg/kg in adult patients with active AS showed significant improvements in sleep problems, TBP and NBP. It was also demonstrated that NBP improvement was associated with improvement in sleep problems. |
 |
|
You are receiving this email because your contact is in the database of V·Pulse subscribers. The content and web links contained in this email may be promotional in nature. Do not reply to this email. If you have a question, please email v.pulse@vital-base.com We respect your right to privacy.
To ensure delivery to your inbox (not junk or bulk folders), please add v.pulse@vital-base.com to your address book. CONFIDENTIALITY NOTICE: This email message (including all attachments) is for the sole use of the intended recipient(s) and may contain confidential information. Any unauthorized review, use, disclosure, copying or distribution is strictly prohibited. If you are not the intended recipient, please contact the sender by reply email and destroy all copies of the original messages © 2020 Vital Base International Limited. All Rights Reserved. |