Pistachios have quickly risen to fame in the world of sweets, but their benefits may extend beyond culinary delight. Lutein and zeaxanthin are dietary xanthophylls that cross the blood-brain barrier to accumulate in the retina as macular pigment (MP) and improve visual function, which is particularly important in preventing conditions like age-related macular degeneration. Despite being commonly found in green leafy vegetables, the lipid-soluble nature of lutein and zeaxanthin results in low bioavailability and poor intestinal absorption. Pistachios, being relatively high in fat, serve as ideal carriers for lutein and zeaxanthin with potentially enhanced bioavailability. The effects of pistachio consumption on MP optical density are evaluated in a randomized controlled trial, where participants in the intervention arm were given 57 g of pistachios in addition to their usual diets5. At the end of the 12-week trial, those in the intervention arm experienced a highly significant increase in MP optical density compared to baseline levels. Those in the placebo arm, having only maintained their usual diets, exhibited no significant changes in MP optical density. The stark contrast in MP optical density between the two arms can be clearly observed in Figure 1. Another parameter measured in this study, sure to pique public interest, is the impact of increased daily pistachio consumption on weight change. Reassuringly, no significant weight changes were observed in either group throughout the trial. Although further research will be needed to solidify the benefits of pistachio consumption for eye health, these encouraging results unveil the potential advantages of incorporating pistachios into a healthy diet.
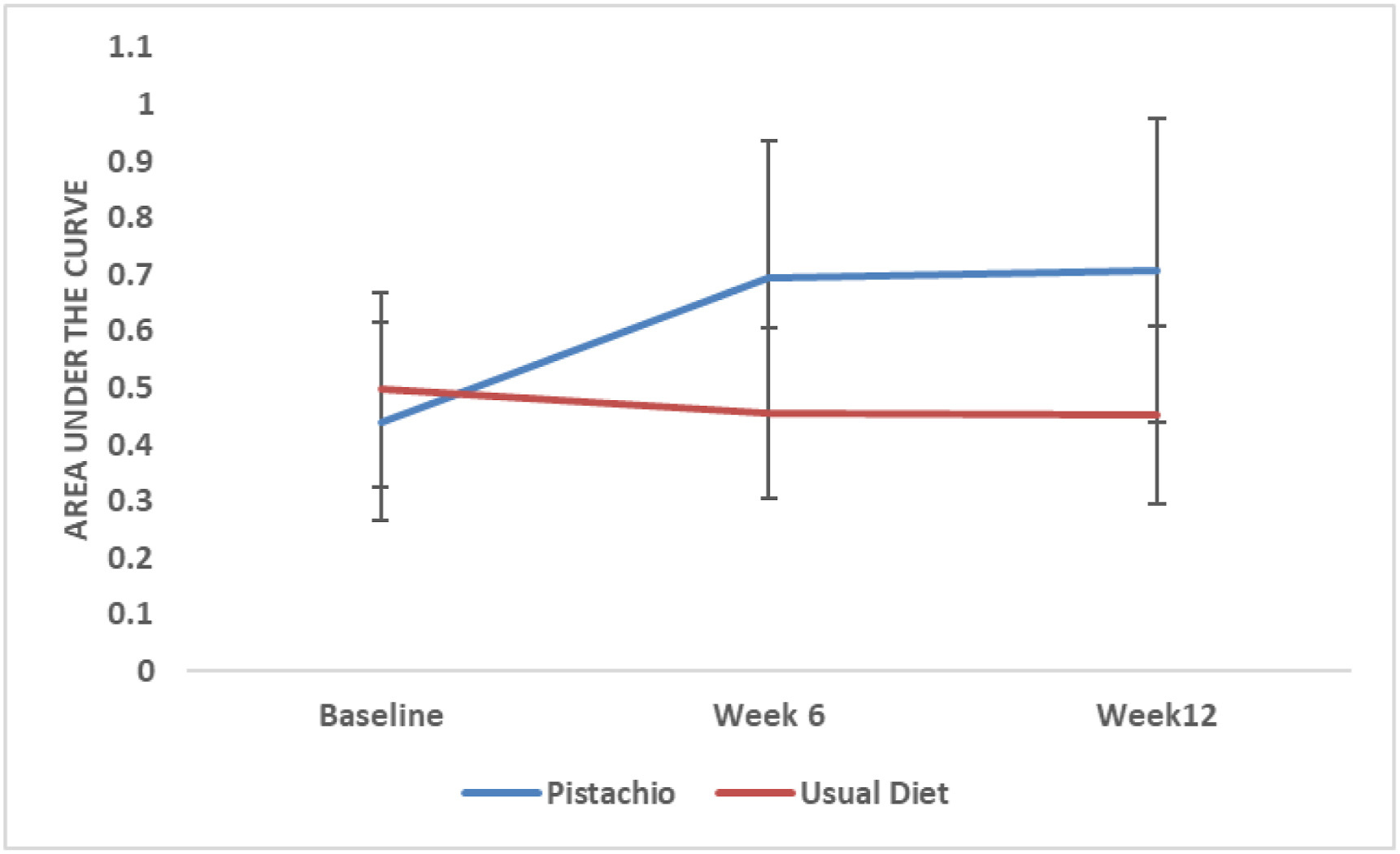
Figure 1. Area under the curve of macular pigment optical density in the two intervention arms.
References
1. Qeadan F, et al. Addiction [Internet]. 2024 Oct 16; Available from: https://doi.org/10.1111/add.16679
2. Rejoyn Clinician Brief Summary [Internet]. Rejoyn. 2024. Available from: https://www.rejoynhcp.com/Clinician-Brief-Summary.pdf
3. Woolley MG, et al. Cognitive Behaviour Therapy. 2024 Apr 15;1–15.
4. Forbes A, et al. 2023 Jun 28;25:e43727.
5. Scott TM, et al. Journal of Nutrition [Internet]. 2024 Oct 1; Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tjnut.2024.10.022





